In software product development, ideas transform into tangible solutions two terms often stand at the forefront: Prototype and Minimum Viable Product (MVP). Both play essential in creating successful products, but they are different in what they aim for and how they are done. It is important for entrepreneurs, product managers, and development teams what development techniques to choose are most important. In this blog, we will delve into the difference between prototypes and MVPs, helping you understand which one is the optimal choice for your project.
What is a Prototype?
A prototype is an early stage or release of your product that tests a design concept before launch. It tests the ideas and changes of a new design until the final product appears. You can check features, user interactions(UI), and overall user experience(UX) can be evaluated against the fully developed product. It allows designers to validate concepts by gathering feedback from real users, rather than committing to a full-design cycle based on assumptions.
Benefits of Prototype
- Stakeholders can understand the product’s concept and functionalities easily.
- Earlier feedback from users, allows designers to identify errors and enhance the product before completion.
- Finding the issues in the prototyping stage is more cost-effective than post-development fixes.
- The iteration accelerates the development cycle and brings the products to market faster.
- Prototyping fosters user-centered design, ensuring alignment with user needs.
- Prototypes show a product’s features and functionalities to potential investors, partners, or customers, helping to generate interest and support.
- Teams can validate assumptions and hypotheses about the product’s design and functionality through real-world testing and user feedback.
What is MVP?
MVP stands for Minimum Viable Product, which is a version of a product with just enough features to satisfy early customers and provide feedback for future product development.
It allows businesses to test their ideas in the market with minimal resources and gain valuable insights from real users. MVPs function as a platform for testing ideas, collecting feedback, and making informed decisions for future development.
Example of a Minimum Viable Product
A ride-sharing service like Uber offered only basic features like requesting a ride, tracking the driver’s location, and making payments. By focusing on these essential functions, Uber could test its service in the market, gather feedback, and then gradually add more features like ride-sharing, different vehicle options, and advanced payment methods based on user demand and usability insights. This iterative approach allows companies to validate their product idea, refine it based on real-world usage, and ultimately deliver a more polished and valuable product to customers.
Benefits of an MVP
Minimum Viable Product offers several advantages. Here are the few advantages
- Launch your product quickly with only essential features. This reduces development time and faster time to market.
- By releasing a basic version of your product, you can gather feedback from real users for understanding user needs and guiding future iterations.
- Developing only the core features required for an MVP minimizes initial development costs
- After launching the initial version, you can continuously iterate and improve based on user feedback and market demands.
- MVP helps you to prioritize features based on their value to users which benefits by avoiding unnecessary complexity.
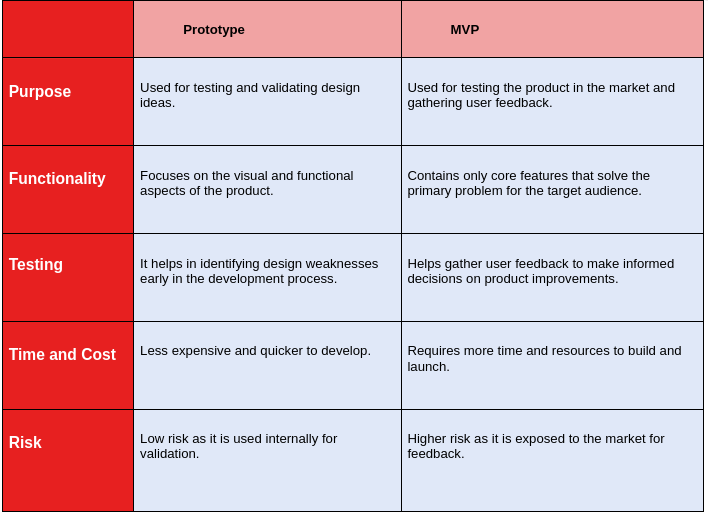
Difference Between Prototype vs. MVP
How To Select Between an MVP and a Prototype?
When deciding between a prototype and an MVP, consider the following factors:
- Stage of Development: If you are in the early stages of concept validation, a prototype may be more suitable. Alternatively, if you possess a well-developed product concept and are prepared to test it in the market, an MVP might be more advantageous.
- Market Validation: If you need to test the product in the market and gather user feedback, an MVP is the way to go.
- Budget and Time Constraints: An MVP is like a simple version of your product with the main features to test if it works and get feedback from users. It’s good when you have a small budget and want to launch quickly. A Prototype shows how your product will look and work. It’s used in the early stages to get support or money. Consider a prototype when you are creating a complex prototype.
Conclusion
Both Prototype and MVP have their unique advantages. The choice depends upon your project’s goal, stage of development, market validation, time and budget, etc. Remember, the key to success lies in understanding your target audience, catering to their needs, and iterating on your product to meet their expectations. Remember, both approaches are crucial milestones in a successful product launch. If you aim to develop a product for your business, reach us at info@authorselvi.com for further information. We are here to help!